Powder Metallurgy Processes
Overview of Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy (PM) is a distinctive metal processing technology that involves the production of metal powders and the conversion of metal powders or mixtures of metal and non-metal powders into practical products through shaping, sintering and other techniques. It is a process that manufactures special materials and precision mechanical components by producing metal powders and applying shaping and sintering technologies to turn powders or their mixtures into usable products. Not only is it suitable for manufacturing special materials that are difficult to obtain via conventional smelting methods, but it also enables the production of precision mechanical parts, achieving the goals of labor and material saving. However, this technology has certain limitations, such as the relatively high cost of molds and metal powders, and it is not suitable for manufacturing products with small batch sizes or excessively large dimensions. Nevertheless, compared with traditional material processing technologies, powder metallurgy materials and processes still demonstrate unique advantages.
Powder metallurgy: the core principle of “making gold from powder”
Powder metallurgy can be called the “metal ceramic method”, and its core is to achieve component manufacturing through four major steps: powder milling, forming, sintering, and post-treatment. First, metal or alloy powder is produced through atomization, reduction, and other methods, and then the powder is pressed into a specific shape. Finally, the powder particles are sintered at high temperature to form a dense structure through diffusion and welding, ultimately obtaining high-precision products. This process has a metal utilization rate of over 95% and can
also manufacture complex components that traditional casting and forging cannot achieve.

Key Characteristics of Powder Metallurgy
A defining feature of powder metallurgy processes is that they are carried out at temperatures below the melting point of the base metal. This allows for the production of special functional composite materials and products with multiphase inhomogeneities, including various metals with significant differences in melting point and density, as well as metal-ceramic and metal-plastic composites. Conducted at temperatures below the melting point of the base metal, powder metallurgy enables the preparation of special composite materials, enhances material performance and utilization efficiency, and reduces machining volume. Fine metal or alloy powders produced by special methods feature rapid solidification rates and fine, uniform grain sizes, thus ensuring uniform material microstructure, stable performance, and excellent cold and hot working properties.
Application Fields of Powder Metallurgy
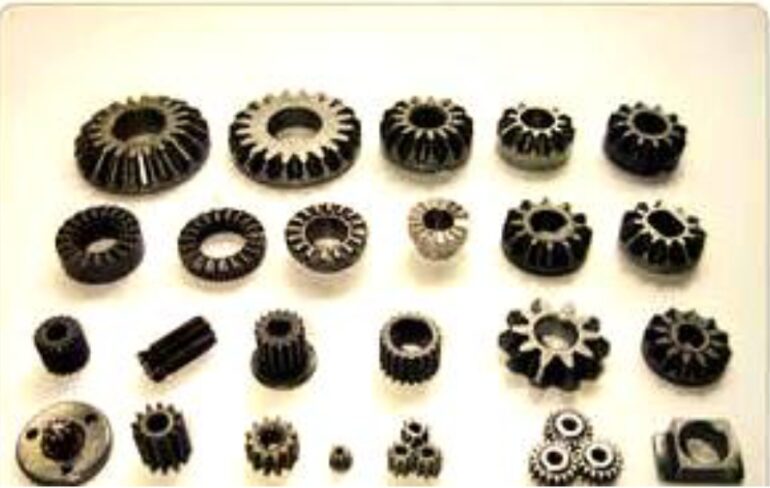
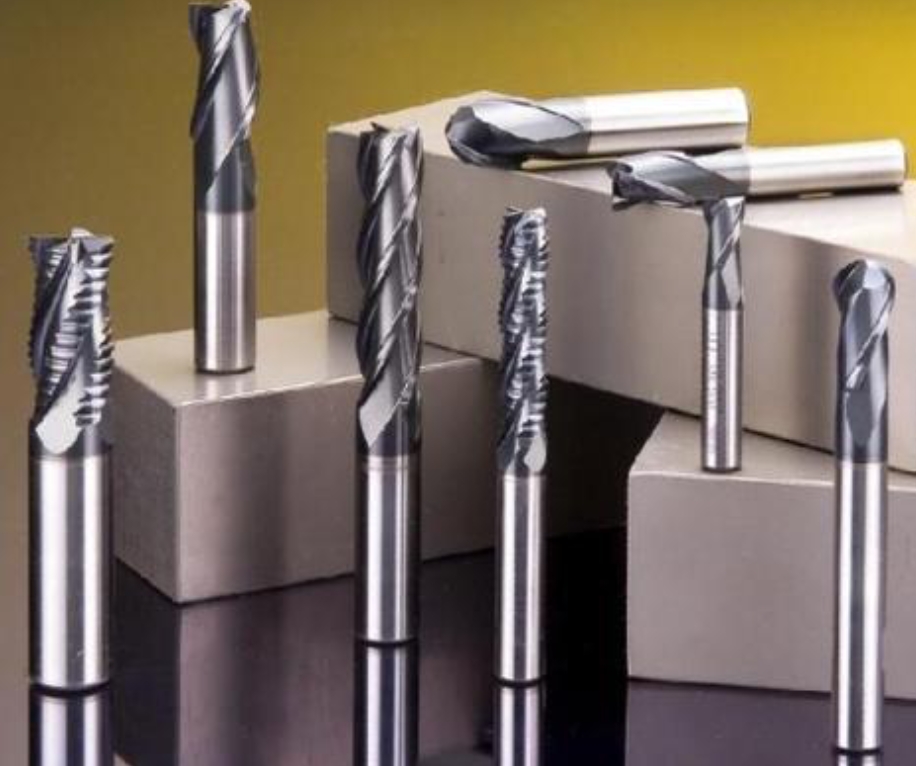
Powder metallurgy has a wide range of applications, including the manufacture of refractory metal products and alloys such as tungsten. In addition, the process involves the preparation of cemented carbides such as tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TiC) and tantalum carbide (TaC). These alloys are commonly used in the production of cutting and wear-resistant tools such as drills, turning tools and milling cutters, and even for mold manufacturing. Meanwhile, porous materials such as copper alloys, stainless steel and nickel are also important powder metallurgy products, which play a key role in the manufacture of sintered oil-impregnated bearings, sintered metal filters and textile rings. Powder metallurgy is widely used in the production of refractory metals, cemented carbides, oil-impregnated bearings, filters and other products, providing important support for modern manufacturing industry.

Powder Preparation and Manufacturing Processes
Powder Preparation Methods
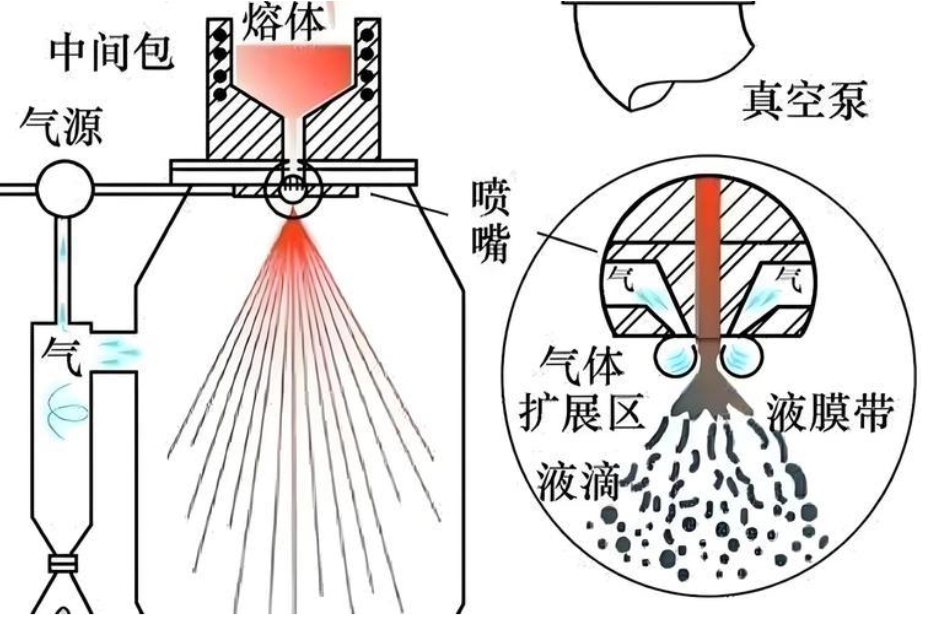
The chemical composition of metal powders is of crucial importance. Commonly used metal powders include iron, copper, aluminum and their alloys, and the content of impurities and gases in these powders must be strictly controlled, usually requiring no more than 1% to 2%. Metal powders can be prepared by mechanical methods and physicochemical methods, and different methods affect powder characteristics and subsequent process performance. In recent years, advanced ultrafine powder manufacturing technologies have also emerged, such as mechanical alloying, amalgamation, evaporation and ultrasonic comminution.
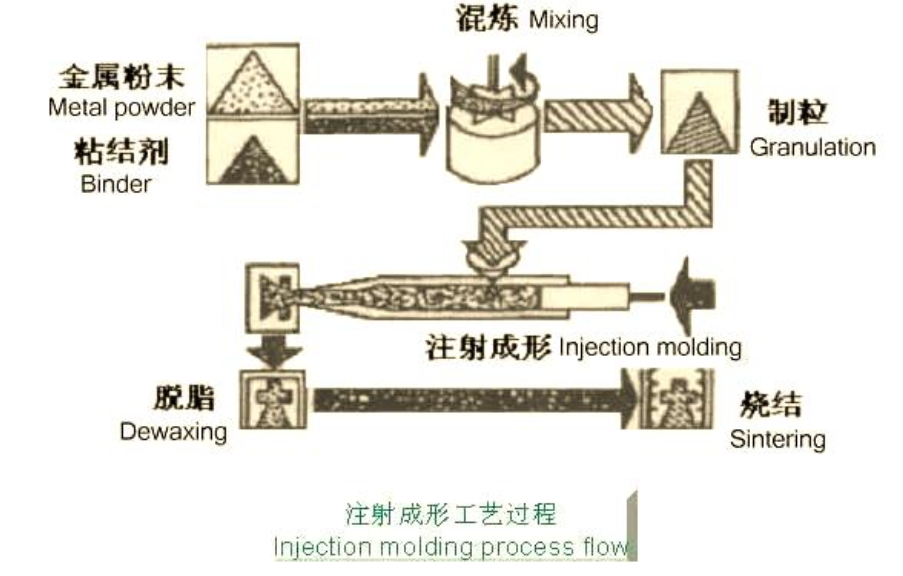
Powder Pretreatment
Prior to application, powders often undergo a series of pretreatment steps, such as annealing, classification, mixing, granulation and lubricant addition. Powders need to be pretreated through annealing, classification, mixing and other processes to optimize their physical and chemical properties for specific applications.

Shaping Processes
Shaping is a key step in the powder metallurgy process, which involves converting pretreated powders into agglomerates with specific shapes. Shaping processes include die pressing, rolling, extrusion and others, which transform powders into specific shapes to meet different application requirements. For example, die pressing is a process where metal powder is filled into a mold and formed into a compact under pressure.
Sintering Processes
Sintering is another important step in powder metallurgy, and its methods vary according to product performance and raw material composition. Sintering promotes metallurgical bonding between powder particles through heat treatment, enhancing material strength, and the process can be adjusted according to raw materials and product performance requirements. During the sintering process, as the temperature rises gradually, a series of complex physical and chemical changes occur inside the powder or compact.
Post-treatment
After the completion of sintering, post-treatment is often required to meet the specific requirements of the product. Post-treatment processes such as repressing and heat treatment are designed to adjust product characteristics to meet the requirements of their final applications. These post-treatment methods include repressing, impregnation, heat treatment, surface treatment and cutting.
Powder Metallurgy Parts and Materials
Processability of Powder Metallurgy Parts
In the field of powder metallurgy, the commonly used method for part forming is compressing metal powders in rigid closed molds. However, this method entails relatively high mold costs. At the same time, due to the poor fluidity of metal powders and the effect of friction, the resulting compacts tend to have low density and uneven density distribution, which in turn leads to insufficient overall strength of the parts. The design of powder metallurgy parts needs to adopt simple and symmetrical shapes and avoid complex structures to ensure smooth forming and reliable use.
Applications of Powder Metallurgy Materials
Powder metallurgy materials have a wide range of applications, including tool materials, mechanical parts and structural materials. In terms of tool materials, there are numerous options such as powder high-speed steel, cemented carbide, superhard materials, ceramic tool materials and composite materials. For mechanical and structural materials, they include powder antifriction materials (further divided into porous and dense antifriction materials), powder metallurgy iron-based parts and powder metallurgy non-ferrous metal parts and other diversified products. Powder metallurgy is widely applied in the fields of tools, mechanical parts, structural materials and others, covering a variety of products such as high-speed steel and cemented carbide.

About mdm metal
Mdm Metal Company focuses on the research and development, production, and sales of powder metallurgy new materials and components. Its products are mainly used in the fields of automobiles (including new energy vehicles), household refrigeration compressors, motorcycles, power tools, office machinery, engineering machinery, and consumer electronics. Mdm Metal is one of the largest powder metallurgy machinery parts manufacturing enterprises in China, using the world’s most advanced surface gloss measuring instruments for quality and appearance inspection, product quality is guaranteed, with a leading market share in the Chinese powder metallurgy market and long-term ranking first in the industry. The company is a national key high-tech enterprise, with a domestic market share of about 20.5% in the powder metallurgy (P&S) field and a leading position in the metal injection molding (MIM) field.
Learn more https://mdmmetal.com/about/






